Can you get cured of Asthma?
No specific cure exists for Asthma to date. Yet, it’s an extremely manageable condition. A few physicians say today’s asthma treatments are so safe and efficacious, that many individuals have near-whole control of their signs.
What is Asthma?
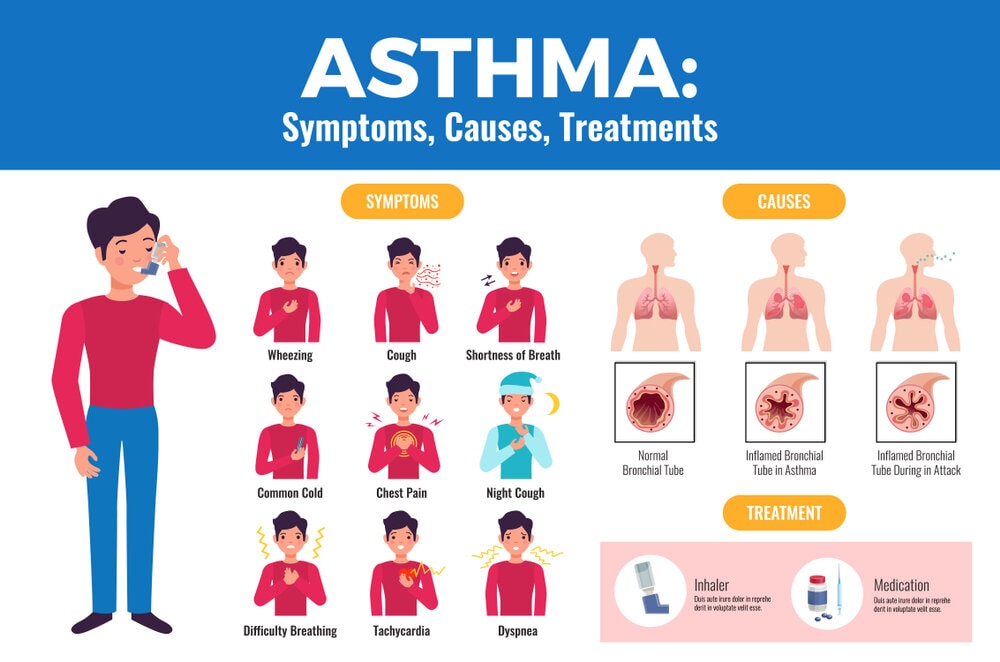
Asthma is a medical problem that results in the narrowing and swelling of the airways. It might also produce extra mucus. This might increase breathing troubles and trigger coughing, a shrieking sound (wheezing) while exhaling. For a few individuals, asthma is a minor irritation. For others, it might turn into a serious issue that starts interfering with your daily activities. Also, it might lead to a life-threatening asthma attack.
What is an Asthma attack?

Inhalation of air results in relaxation of the airway muscles. And, this lets air move freely and quietly. 3 things occur during an asthma attack and these are:
Inflammation:
The airway lining gets inflamed. Inflamed airways don’t permit as much air in or out of your lungs.
Bronchospasm:
The airway muscles tighten or constrict. Constriction results in the narrowing of the airways. Air cannot flow easily through the narrowed airways.
Production of Mucus:
Throughout the attack, your body produces more mucus. This thick mucus blocks airways.
Tightening of the airways produces a sound called wheezing while you inhale air. Wheezing is a type of sound your airways make when you exhale air. Also, you may hear an asthma attack named an exacerbation or an outbreak.
So, the question is, is it possible to cure asthma completely?
There is no overall asthma cure. However, a person can control it to the point that the signs become insignificant. As a long-term health condition, asthma is not treatable. It is extremely treatable, even if a patient has specialized support.
Asthma Symptoms:

The signs may differ from individual to individual. You might experience uncommon asthma attacks, have signed only at certain times including while exercising, or experience signs all the time.
Asthma symptoms can be:
- Chest pain or tightness
- Breathing difficulty
- Wheezing when breathing out (a common symptom of asthma in kids)
- Coughing or wheezing attacks exacerbated by a respiratory virus like a cold or the flu
- Sleeping problems due to breathing troubles, coughing or wheezing
For a few individuals, asthma causes outburst in certain conditions:
- Exercise-induced Asthma(might deteriorate when the air is cold and dry)
- Occupational Asthma(activated by workplace irritants like dust, chemical fumes, or gases)
- Allergy-induced Asthma(activated by airborne materials like pollen, mold spores, and cockroach waste).
What causes Asthma?
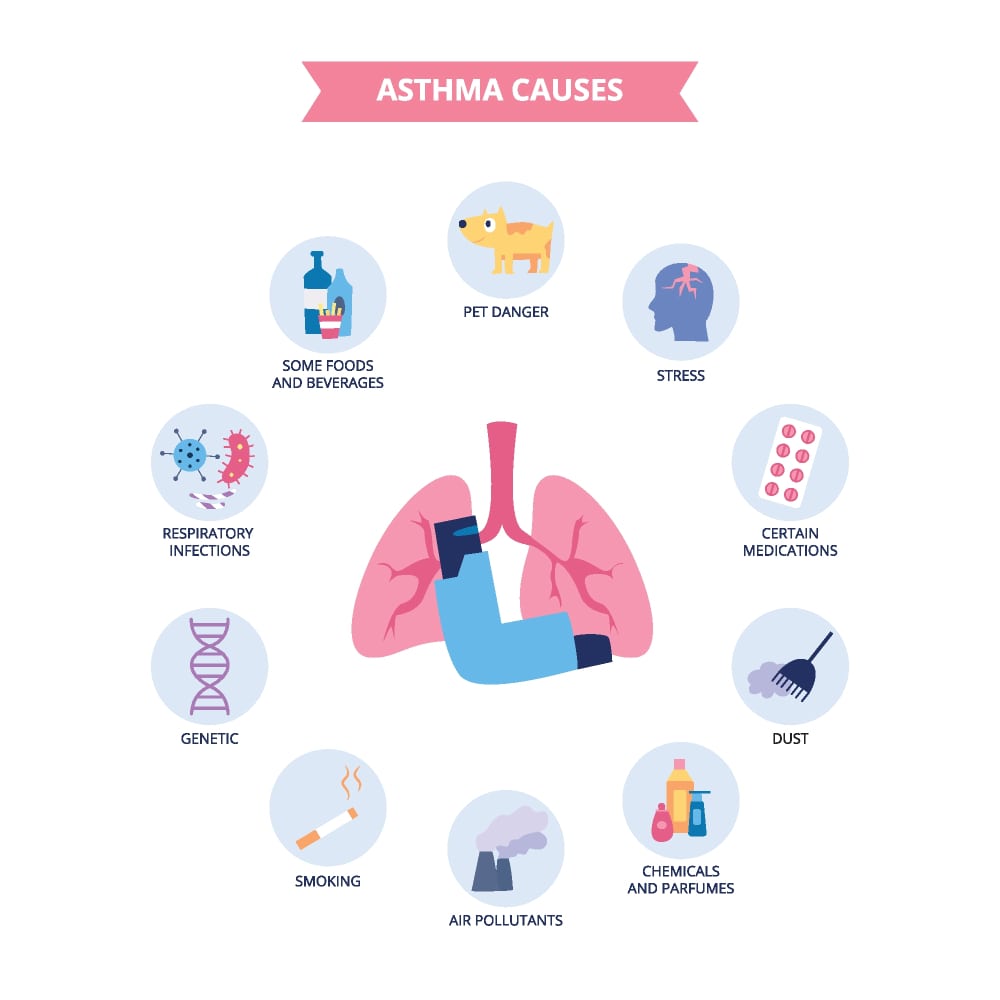
Common triggers can be:
- Air pollution
- Tobacco smoke
- Infections such as cold or flu
- Allergens like pollens, mold, dust mites
- Exercise
- Irritants such as strong odors from perfumes
- Cold air or climate changes, such as temperature or humidity
- Strong emotions like anxiety, stress
- Medicines like aspirin
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Food preservatives referred to as sulfites (present in shrimp, bottled lime juices, pickles, beer and wine, and dried fruits)
What Types of Asthma are there?
Asthma is a complicated medical disorder owing to its many subtypes and classifications according to its origins, symptoms, and reaction to therapy. The following are some of the primary categories and forms of asthma:
- Allergic Asthma: Caused by allergens including mold, dust mites, pollen, or pet dander. frequently connected to changes in the seasons or exposure to particular allergies.
- Non-Allergic Asthma (Intrinsic Asthma): This type of asthma is not brought on by allergens; instead, it is brought on by stress, respiratory infections, smoking, and weather variations. It could be more difficult to diagnose and can happen without a recognized allergy cause.
- Exercise-induced asthma (EIA): Physical exertion, particularly in dry, cold air, can aggravate symptoms.
- Occupational asthma: Occupational asthma is brought on by allergies or irritants encountered at work. may get better when you’re not at work, but when you get back, it can get worse.
- Cough-variant: Cough-variant asthma is defined by a persistent cough as the primary symptom, with little to no wheezing or dyspnea. Prolonged coughing may be brought on by respiratory illnesses, exertion, or cold air.
- Nighttime Asthma: Nighttime Asthma At night, symptoms start or get worse. includes coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath that wakes you up and can interfere with your sleep.
- Severe asthma: Severe asthma that needs more extensive care and does not respond well to conventional therapies.
- Asthma: Asthma is caused by variations in the seasons, especially when certain allergies are more common. frequently falls at certain seasons of the year, such as spring or fall, when pollen counts are at their highest.
- Aspirin-Sustained: Aspirin-Sustained The use of aspirin or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) can cause or exacerbate asthma symptoms.
- Eosinophilic asthma: Eosinophilic asthma is linked to higher blood levels of eosinophils, a kind of white blood cell implicated in inflammatory reactions. Frequently associated with more severe asthma, these conditions may need specialized care, such as biologics.
Craft your Asthma action plan:
What triggers asthma? Asthmatic patients have highly individual responses and triggers. Healthcare providers think that there are many asthmas, each with its causes, risks, and treatments. If you have asthma, your physician will work with you to produce an asthma action plan.
This plan concentrates on your signs and the substances that activate them. The plan would likely involve alterations in your environment and activities, in combination with medication to help you manage your signs.
Asthma Diagnosis:

Physical assessment:
Your healthcare provider would carry out a physical assessment to exclude other possible conditions. These conditions can be chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or respiratory infection. Moreover, your doctor would ask you queries concerning your signs and about any other medical conditions.
Tests to evaluate lung function:
You might be ordered certain lung function tests to depict how much air moves in and out as you inhale air. These tests might be:
- Lung function tests: are performed before or after using medicine to open your airways called a bronchodilator like albuterol. If there is an improvement in lung function upon using a bronchodilator, you may have asthma.
- Peak flow: A peak flow meter is an easy device that assesses how hard you can exhale air. Below normal peak flow readings are an indication that your lungs might not be functioning as well and your asthma is deteriorating.
- Spirometry: This test assesses the narrowing of your bronchial tubes by examining the amount of air you breathe out after a deep breath and how fast you can exhale.
Treatment of Asthma:

Asthma treatment serves 2 major purposes: short-term signs relief and long-term control. Here are a few asthma medications your doctor might add to your asthma action plan:
Inhalers:
These portable devices provide a premeasured dose of asthma medication into your lungs. These are J-shaped pumps. You need to hold them to your mouth and push down on the canister. The pump pushes a mist or powder that you breathe in. There are different types of inhalers for asthma available at the best prices on OffshoreCheapMeds such as Advair, Spiriva, Anoro Ellipta, Flovent, Symbicort, etc.
Some inhalers comprise corticosteroids that control irritation and inflammation in your airways. These inhalers work for daily use or seasonal use. Other inhalers comprise fast-acting medications including beta 2 agonists, bronchodilators, or anticholinergics.
These medications may open your airways rapidly if you’re experiencing an asthma outbreak. A few inhalers might consist of a combination of medications to regulate your specific reactions.
Nebulizers:
These separate devices turn liquid medication into a mist you can inhale. The medications that are utilized in these lower inflammation and irritation in the airways.
Oral medicine for asthma treatment:
Your long-term action plan might also involve oral medicines. Oral asthma medicines are leukotriene modulators (which decrease inflammation) and theophylline (which are substituted with safer, more effective drugs). Both of them open your airways and people consume them in pill form. Oral corticosteroid tablets are also at times chosen.
Biologics:
You might have an injection of a biological drug one or two times a month. These medications are also known as immunomodulators. As they lower certain WBCs in your blood or decrease your sensitivity to allergens in your atmosphere.
Quick-relief (Rescue) Drugs:
These are useful for fast, short-term relief of signs throughout an asthma attack. People might also use them before exercise if their physicians suggest them. Types of quick-relief drugs can be:
- Anticholinergic agents: Similar to other bronchodilators, ipratropium, and tiotropium work instantly to relax your airways. This makes it simpler to inhale air. They are helpful for emphysema and chronic bronchitis, however, may be used for asthma.
- Short-acting beta-agonists: These inhaled, quick-relief bronchodilators work within minutes to quickly relieve signs during an asthma attack. They can be albuterol and levalbuterol.
- Oral and iv corticosteroids: These drugs involve prednisone and methylprednisolone. And, help ease airway inflammation due to severe asthma. They may lead to severe side effects when used long-term. Hence, such medications should be used only on a short-term basis to manage serious asthma symptoms.
Bronchial Thermoplasty:
This treatment of asthma is useful for severe asthma that fails to be managed via inhaled corticosteroids or other long-term asthma drugs. It isn’t extensively available or appropriate for every person.
During this procedure, your healthcare provider heats the interior of the airways in the lungs using an electrode. The heat decreases the smooth muscle present in the airways. This restricts the capability of the airways to constrict. And, makes breathing simple and lowers asthma attacks. The therapy is usually performed over 3 outpatient visits.
How to Cure Asthma Permanently?
A combination of medication and lifestyle modifications can effectively manage and control asthma. The most popular long-term Inhaled corticosteroids drugs help lower airway inflammation and are advised in conjunction with long-acting beta antagonists.
Medication called a leukotriene modifier aids in lowering inflammation and averting asthmatic symptoms. Determine which allergens—such as pollen, dust mites, mold, pet dander, smoking, strong scents, and other irritants—can aggravate asthma symptoms and reduce your exposure to them. Regularly performing moderate exercise can help reduce the symptoms of asthma and enhance overall lung function.
Keeping a healthy weight in mind and maintaining regular follow-up consultations with your healthcare practitioner to develop an asthma action plan that describes how to reduce symptoms, evaluate your asthma control, and modify your treatment plan as needed.
Although there isn’t a long-term asthma treatment, you may live a happy, active life and effectively manage your illness with the aid of these measures. You must collaborate closely with your healthcare team to customize a management plan that meets your specific requirements.
Home remedies for Asthma:

How to prevent asthma? There are a lot of natural remedies to consider.
Caffeine:
Caffeine is a natural remedy for asthma as it is associated with the drug theophylline. It helps relax the airway muscles. Studies suggested that intake of coffee resulted in mild improvement in airway working for up to 4 hours.
Omega-3 Oils:
Omega-3 oils are present in fish and flax seeds. And, these oils have been found to comprise a lot of health benefits. They might also function to reduce airway inflammation and improve lung function in individuals experiencing severe asthma. High doses of oral steroids might inhibit the useful effects of omega-3 oils.
Ginger:
Ginger is a herb that has strong anti-inflammatory properties and might assist in severe asthma. A study found that oral ginger supplements were associated with an improvement in asthma symptoms. However it didn’t verify that ginger causes an improvement in complete lung function.
Garlic:
Garlic is a herb with numerous health benefits, such as anti-inflammatory properties, as per a recent study. As asthma is an inflammatory medical problem, garlic can be useful for easing your symptoms. Also, garlic is efficacious in preventing asthma outbursts.
Vitamin D:
A supplement is usually combined with your asthma medicines. It is seen to reduce the risk of going to the emergency room for an asthma attack by 50%.
Yoga:
Yoga integrates breathing and stretching exercises to help improve flexibility and augment your overall fitness. For a lot of individuals, practicing yoga may reduce stress, which may activate your asthma. The breathing approaches used in yoga might also aid in lowering the incidence of asthma attacks.
Asthma is a medical problem that results in narrowing your airways due to swelling, tightening, or increased mucus. While there’s no treatment, there are a lot of treatment options that might manage and prevent flare-ups or cure signs when they crop up. A few natural or home remedies are of great help. And, it is possible to cure asthma with diet. Make sure to discuss this with a doctor before including anything in your asthma action plan.
A successful treatment demands a routine symptom tracker and assessing the working of the lungs as well. Effective asthma management helps you maintain improved long-term asthma control and avoid asthma attacks.
FAQs:
Why is Asthma worse at night?
The most common reasons for worsening asthma during the night:
- Exposure to allergens such as bedbugs, dust mites, or pet dander. All occur commonly in the bedroom and may activate asthma attacks.
- Postnasal Drip: When you lie flat, it is simple for fluid to drip down the back of your throat and resulting in coughing.
- Supine position and acid reflux
- Circadian modifications in lung function. Our lungs function differently during the night. Airway resistance augments during the night, and this effect is more distinct in people with asthma.
- Medicine Timing: If your medicine wears off during the night, you’re expected to experience nocturnal asthma.
Can smoking result in Asthma?
One of the most common triggers of asthma is tobacco smoke. Tobacco smoke like second-hand smoke is not healthy for any person, particularly for asthmatics.
Where does Asthma come from?
Exposure to irritants or substances that activate allergies (allergens) might trigger asthma symptoms. Asthma triggers vary from individual to individual. And, these may involve Airborne allergens including pollen, cockroach waste, dust mites, pet dander, or mold spores.
Does Asthma cause chest pain?
If you experience asthma, you may also have chest pain. This sign is common before or during an asthma attack.
Can stress cause Asthma?
Strong emotions and stress are common triggers of asthma. There is substantial data associating asthma, anxiety, and depression.
What drink is good for asthma?
Various herbal teas are useful for relieving the signs of asthma. The research proposes that ginger tea, fennel tea, black tea, eucalyptus tea, green tea, and licorice tea help relieve inflammation, relax the respiratory muscles, and improve breathing.
Does Asthma shorten your life?
A study found that asthma reduced life expectancy by 3 years, similar to the effect of smoking.
Is Asthma lifelong?
It is a chronic (or lifelong) medical problem that might be severe, even life-threatening. There is no cure.
Can Asthma be cured by exercise?
Regular exercises help reduce symptoms by improving your lung health. The most important thing is to do the correct type and amount of physical activity. You can depict what this looks like for you by discussing it with a concerned doctor.
What is the best treatment for Asthma?
Long-term control medications such as inhaled corticosteroids are the most important medications used to keep asthma under control. These preventive medications treat the airway inflammation that leads to asthma symptoms. Used daily, these medications can reduce or eliminate asthma flare-ups.

